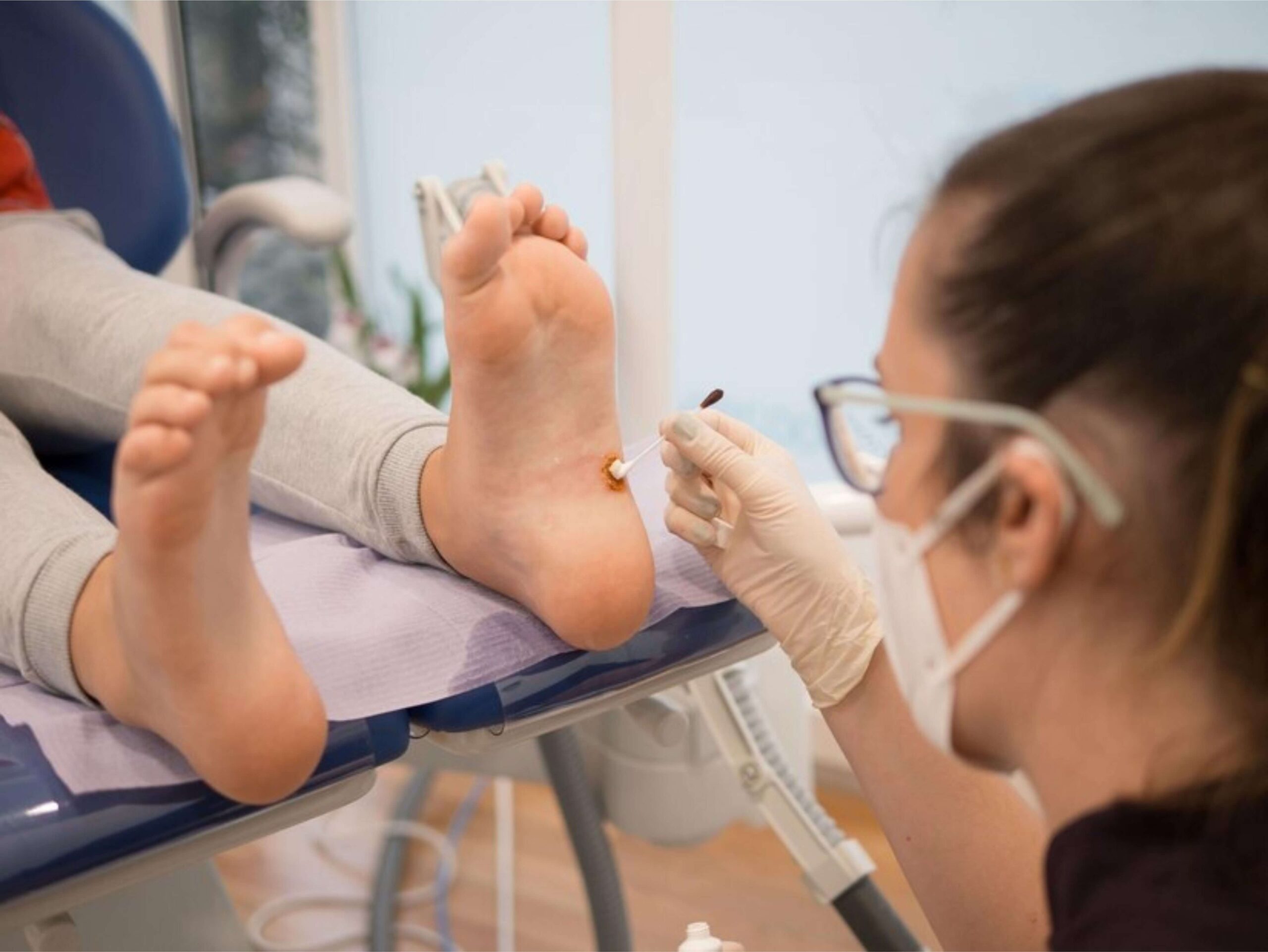
DIABETIC FOOT ULCER
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are a common and serious complication of diabetes mellitus. They pose a significant threat to the health and well-being of individuals living with diabetes. Understanding the causes, treatment options, and preventive measures is crucial in managing this condition effectively.
Causes: DFUs develop primarily due to two factors: neuropathy and peripheral vascular disease. Neuropathy, or nerve damage, reduces sensation in the feet, making it difficult for individuals to detect injuries or pressure points. Peripheral vascular disease diminishes blood flow to the extremities, impairing the body’s ability to heal wounds.
Other contributing factors include:
- Prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels
- Poor circulation.
- Foot deformities.
- Trauma or injury to the foot.
- Poorly fitting footwear.
- Impaired immune function.
Treatment: The management of DFUs requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals such as podiatrists, endocrinologists, vascular surgeons, and wound care specialists. Treatment strategies may include:
- Wound Debridement: Removal of dead or infected tissue to promote healing.
- Offloading: Relieving pressure from the affected area to prevent further damage.
- Dressings and Topical Treatments: Application of specialized dressings or topical medications to facilitate healing and prevent infection.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed to treat or prevent infection.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions such as skin grafts or amputation may be necessary.
Prevention: Preventing DFUs is essential in diabetic foot care. Here are some preventive measures individuals can take:
- Maintain Proper Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping blood glucose levels within the target range can reduce the risk of neuropathy and vascular complications.
- Inspect Feet Daily: Regularly check feet for any signs of injury, redness, blisters, or cuts.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Choose shoes that fit well and provide adequate support and cushioning.
- Practice Good Foot Hygiene: Wash feet daily with mild soap and warm water, and thoroughly dry them, paying attention to the areas between the toes.
- Avoid Going Barefoot: Always wear shoes or slippers to protect feet from injury.
- Regular Foot Exams: Schedule regular foot exams with a healthcare professional, especially if you have existing foot problems or are at high risk for complications.
Diabetic foot ulcers can have serious consequences if left untreated. By understanding the causes, seeking prompt medical attention, and implementing preventive measures, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage this condition and reduce the risk of complications. Remember, proactive foot care is key to maintaining overall health and quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.